URL: http://ctf.asis.io/challenges/1005/
Type: XOR + byte nibbles shifting
Solution: ASIS_449e435e4c40dfa726f11b83a07b5471
Description
We have found the cryptor source code. Decrypt the file.
files
Archive cryptor.zip contains 2 files:
Length Date Time Name
-------- ---- ---- ----
787551 08-26-13 16:44 flag.png_Crypted
1427 08-26-13 16:44 cryptor.cpp
cryptor.cpp is the C++ source code of the algorithm used to encrypt the PNG file flag:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <time.h> using namespace std; int bitXor(int, int); int main(int argc, char **argv) { srand(time(NULL)); char *path=new char[30]; if(argc > 1) path = argv[1]; else { printf("\nenter file\n"); scanf("%s",path); } int g = rand() % 512 + 32; int n = rand() % g; int mask = rand() % 256; FILE *inFile = fopen(path, "rb"); FILE *outFile = fopen(strcat(path, "_Crypted"), "wb"); if(inFile == NULL || outFile == NULL) { printf("Error\ncant read/write file\n"); return 1; } unsigned char H, L; unsigned char *readBuffer = new unsigned char[g], *writeBuffer = new unsigned char[g]; while(!feof(inFile)) { int len = fread(readBuffer, 1, g, inFile); if(len < g) fwrite(readBuffer , 1 , len , outFile); else { for(int i = 0 ; i < g ; i++) { int nIndex = i + n; int pIndex = i - n; if(nIndex >= g) nIndex -= g; if(nIndex < 0) nIndex += g; if(pIndex >= g) pIndex -= g; if(pIndex < 0) pIndex += g; H = readBuffer[nIndex] / 16; L = readBuffer[pIndex] % 16; writeBuffer[i] = bitXor(16 * H + L, mask); } fwrite(writeBuffer , 1 , g , outFile); } } fclose (inFile); fclose (outFile); printf("\nsave decryption code: %d.%d.%d\n", g, n, mask); return 0; } int bitXor(int x, int y) { int a = x & y; int b = ~x & ~y; int z = ~a & ~b; return z; }
Algorithm analysis
This is a kind of block cipher. First we identify the meaning of the main variables:
int g = rand() % 512 + 32;32 ≤ g < 544is used as the block fixed-lengthint n = rand() % g;0 ≤ n < gis used as the offset shiftingint mask = rand() % 256;0 ≤ mask < 256is used as the XOR value
In order to understand the encryption algorithm, we can also simplify the source code:
- function
int bitXor(int x, int y)is just a bitwise XOR between the 2 arguments - lines
int nIndex = i + n;…if(pIndex < 0) pIndex += g;can be reduced to:int nIndex = (i + n) % g; int pIndex = (i - n) % g;
H = readBuffer[nIndex] / 16;andL = readBuffer[pIndex] % 16;are dealing with byte nibbles, i.e.His the high nibble ofreadBuffer[nIndex], andLis the low nibble ofreadBuffer[pIndex]writeBuffer[i] = bitXor(16 * H + L, mask);combine the two nibblesHandL
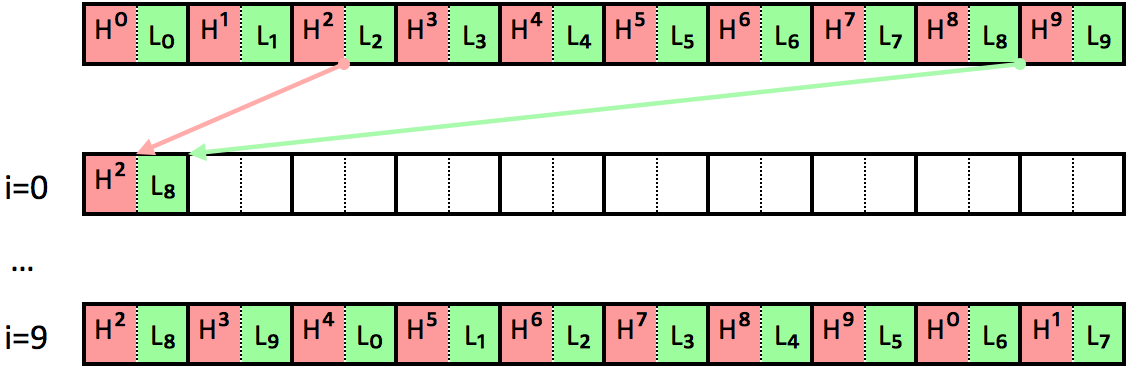
Byte nibbles shifting
Let's have a look how the byte nibbles shifting works with a simple example. Assume block length g = 10 and offset n = 2:
Global specifications
From the algorithm analysis, we can notice:
n= position ofreadBuffer[0]low nibbleg= position ofreadBuffer[0]high nibble + position ofreadBuffer[0]low nibble- if we encrypt data with
g,nandmaskparameters, then decryption process = encryption withg,g-nandmask
Python implementation
Let's define some python functions to manage nibbles operations:
# Extract hi(gh) nibble (4 most significant bits) from a byte def byte2hi_nibble(byte): return (byte >> 4) # Extract lo(w) nibble (4 less significant bits) from a byte def byte2lo_nibble(byte): return (byte & 0x0f) # Extract list of hi(gh) and lo(w) nibbles from a byte def byte2nibbles(byte): return [byte >> 4, byte & 0x0f] # Combine hi(gh) and lo(w) nibbles into a byte def nibbles2byte(hi, lo): return ((hi << 4) | lo)
Simplified encryption algorithm could be:
def encrypt(in_buffer, g, n, mask): out_buffer = '' for block in range(len(in_buffer) / g): tmp_buffer = [0] * g for i in range(g): tmp_buffer[i] = nibbles2byte(byte2hi_nibble(ord(in_buffer[(block * g) + ((i + n) % g)])), byte2lo_nibble(ord(in_buffer[(block * g) + ((i - n) % g)]))) ^ mask out_buffer += ''.join(map(chr,tmp_buffer)) out_buffer += in_buffer[-(len(in_buffer) % g):] return out_buffer
Known Plain Text Attack
The flaw here is that we know from the name of the crypted file that the original one was a PNG image file. Thus we can search for the encryption of the PNG magic number hex sequences:
'\x89PNG\r\n\x1a\n'
- we know that PNG magic number is encrypted in the first bloc (max size = 543)
- we have to check separately the nibbles flows ; PNG magic number high nibbles are contiguous, as are low nibbles, but the two flows may be located at different offsets (
i+nandi-n) - for each position of the bloc, we determine nibble mask value with the first byte of the PNG magic number (using XOR properties (byte ^ mask) ^ byte = mask) ; then we check if the following nibbles XORed with this mask are equals to the nibbles of the full PNG magic number
- we finally compute
g,nandmask(combination of high and low nibbles mask) according to the previous specifications
PNG_MAGIC = '\x89PNG\r\n\x1a\n' PNG_MAGIC_len = len(PNG_MAGIC) PNG_hi_nibble, PNG_lo_nibble = map(list, zip(*[byte2nibbles(ord(c)) for c in PNG_MAGIC])) filename = 'flag.png' f = open(filename + '_Crypted', 'rb') in_buffer = f.read() f.close() # get g max buffer size = 512-1 + 32 / extend to avoid rotation due to n offset < PNG_MAGIC_len gmax = 543 buffer = in_buffer[:gmax] + in_buffer[:PNG_MAGIC_len] buffer_hi_nibble, buffer_lo_nibble = map(list, zip(*[byte2nibbles(ord(c)) for c in buffer])) hi_pos, lo_pos = [], [] for nIndex in range(gmax): # search PNG magic number hi nibbles hi_mask = PNG_hi_nibble[0] ^ buffer_hi_nibble[nIndex] if [(n ^ hi_mask) for n in buffer_hi_nibble[nIndex:nIndex+PNG_MAGIC_len]] == PNG_hi_nibble: hi_pos.append([nIndex, hi_mask]) # search PNG magic number lo nibbles lo_mask = PNG_lo_nibble[0] ^ buffer_lo_nibble[nIndex] if [(n ^ lo_mask) for n in buffer_lo_nibble[nIndex:nIndex+PNG_MAGIC_len]] == PNG_lo_nibble: lo_pos.append([nIndex, lo_mask]) if (len(hi_pos) > 1) or (len(lo_pos) > 1): print 'Magic number is not unique : hi_pos =', hi_pos, ' / lo_pos =', lo_pos else: g = hi_pos[0][0] + lo_pos[0][0] n = lo_pos[0][0] mask = (hi_pos[0][1] << 4) | lo_pos[0][1] out_buffer = encrypt(in_buffer, g, g-n, mask) f = open(filename, 'wb') f.write(out_buffer) f.close()
Running on flag.png_Crypted, we obtain the encryption parameters g = 379, n = 143 and mask = 0xb8, and the following decoded PNG file:


